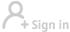Badaling Great Wall
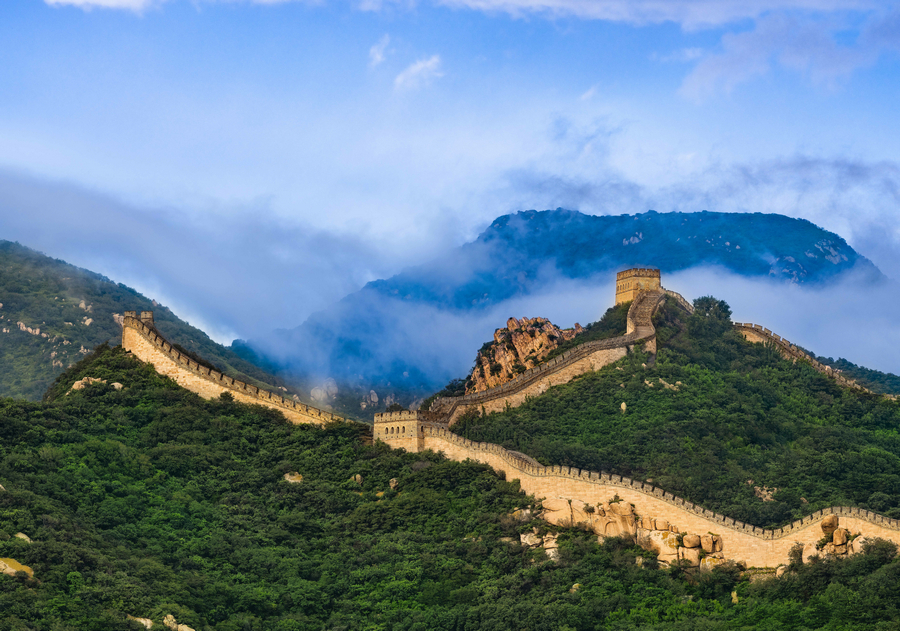


The Badaling Great Wall is located at the northern end of the Guangou Ancient Path in Jundu Mountain, Yanqing district of Beijing. It’s a crucial part of the Great Wall, an extraordinary defensive project in ancient China, as well as an important pass of the Ming Great Wall. As a significant outpost of the Juyong Pass, it was historically noted that “the peril of Juyong Pass lies not in the pass itself but in Badaling”.
The Badaling section of the Great Wall is one of the eighth grand views of the Juyong Pass in Ming Dynasty. Badaling Great Wall is the earliest section of the Ming Great Wall that opened to tourists, and serves as the core of the Badaling scenic area. Modern tourist amenities such as the Badaling Hotel and China Great Wall Museum, inscribed by Chairman Jiang Zemin, have also been built for visitors. Recognized as a National Civilized Scenic and Tourist Area demonstration site, Badaling is famous for its majestic scenery, comprehensive facilities and rich cultural and historical significance, making it a world-renowned tourist destination.
On June 21, 2021, Badaling Great Wall hosted a grand themed light show to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the founding of the Communist Party of China. On the morning of Feb 3, 2022, the torch relay of the Beijing 2022 Olympic Winter Games and Paralympic Games took place at the Badaling Great Wall. In December 2023, the Badaling Great Wall extended its open section for tourists by 1,245 meters - from the South 7th Tower to midway between the South 16th Tower.
The Badaling Great Wall was built in 1505, the 18th year of Emperor Hongzhi's reign during the Ming Dynasty. Over a period of more than 80 years, the construction extended the Wall to over 650 kilometers. General Qi Jiguang, renowned for his defense against Japanese pirates, was later appointed to oversee the Great Wall's defense in Badaling.
In 1953, after the initial renovation of its watchtowers and walls, Badaling was opened to tourists. At present, the open area of Badaling spans 3.741 kilometers, with the south section being 1.176 kilometers and the north section 2.565 kilometers. There are a total of 16 watchtowers within this section.
The most credible explanation for the origin of the name Badaling comes from the Ming Dynasty book “Chang’an Kehua”. According to this book, “The roads from this place branch out in all directions, hence the name Badaling.” As the outer pass of Juyong Pass, Badaling connects to Yanqing, Chicheng and Mongolia in the north; Zhangjiakou, Huailai, Xuanhua and Datong in the west; Yongning and Sihai in the east; and Changping and Beijing in the south. It can thus be said to have access to all directions, making it an important transportation route and defensive outpost in ancient times, earning it the title of "the first barrier of northern Beijing”.