Sharp growth likely for online healthcare sector in China


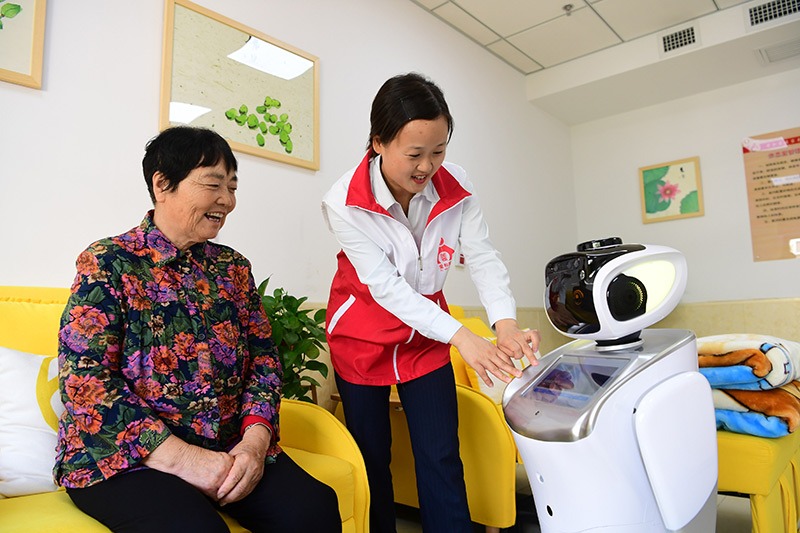
China's online healthcare market is expected to see explosive growth this year as the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the digitalization of the healthcare services industry along with the adoption of state-of-the-art technologies such as 5G and the internet of things.
DXY, a leading online healthcare platform in China, is beefing up efforts to expand its presence in the health industry and planning to march into the internet-based hospital segment as well. The firm will not only provide online consultation services to patients, but also cover content production, chronic disease management, online courses and e-commerce products.
Li Tiantian, founder and chairman of DXY, said the COVID-19 outbreak sped up the online interaction between doctors and patients, the online management of patients, online clinical research and digitalized marketing of medicine.
Li said DXY has provided online courses for doctors, with the number of paid users surpassing 300,000. It has also offered some clinically relevant decision-making tools in a bid to help doctors manage patients and make a diagnosis and offer treatment.
Founded in 2000, DXY already covered over 2 million Chinese doctors, which is about 70 percent of the doctors nationwide. It provides academic discussion, continuing medical education and job recruitment services for medical professionals.
Chu Yang, vice-president of DXY, said the company aims to help pharmaceutical enterprises provide access to more doctors and the public across the nation by virtue of the platform's abundant doctor resources and wide user bases.
A report by consultancy Boston Consulting Group (BCG) said 78 percent of doctors obtained medical information online eight times a week during the epidemic. The number of users who use online and digital medical services reached 620 million, which is close to 70 percent of the total mobile internet users in China.
Chen Baiping, managing director and partner of BCG, said the pandemic has become a catalyst for the digital development of the entire healthcare industry.
Chen noted major pharmaceutical companies have increased their investments in the digitalized construction sector, as only 23 percent of the enterprises saw their expenditures on digitalization accounting for over 10 percent of total products inputs in 2019. This figure has risen to 40 percent in March 2020.
The National Health Commission has pledged to advance the development of online diagnosis and treatment as well as internet-based hospitals. This is expected to help ease the pressure on medical institutions offline and contribute to outbreak prevention and control. The move has led to an exponential increase in the engagement of online medical platforms.
A report by a Beijing-based internet consultancy said the revenue from China's online healthcare industry reached 133.6 billion yuan ($19.1 billion) in 2019, up from 98.5 billion yuan in 2011.
The figure for 2020 will likely be about 200 billion yuan, an increase of 46.7 percent due to the pandemic, Analysys predicted.
Other healthcare apps have created special services where people can converse with doctors online over their symptoms or simply receive more details about preventive measures during the outbreak.
For instance, the number of new users at Ping An Good Doctor, a leading online health service provider, rose nearly 900 percent in January 2020 compared with December 2019.
"The coronavirus epidemic puts a glaring spotlight on the opportunities in digital," said Kevin Chang, head of healthcare practice at Bain & Company China, adding that China's online healthcare platforms have grown sharply as many patients have turned to internet-based options for diagnosis and treatment during the pandemic.
"While some technologies, such as AI-enabled fever-detection devices, are being rolled out quickly in response to the outbreak, other developments such as the widespread adoption of electronic medical records could improve the (healthcare) system's efficiency and transparency in times of crisis," he noted.
Jiang Xinwei, an analyst of Analysys, said the COVID-19 outbreak has greatly expedited the digitization of healthcare infrastructure. The digital medical industry has become one of the most important application scenarios for the technology.
"Meanwhile, offline medical institutions will utilize some cutting-edge technologies to improve the accuracy of medical diagnosis and the quality of patient services in the post-pandemic era. With the development of telemedicine, 5G and virtual reality, the situation of unbalanced and scarce medical resources nationwide will be alleviated to some extent," Jiang said.